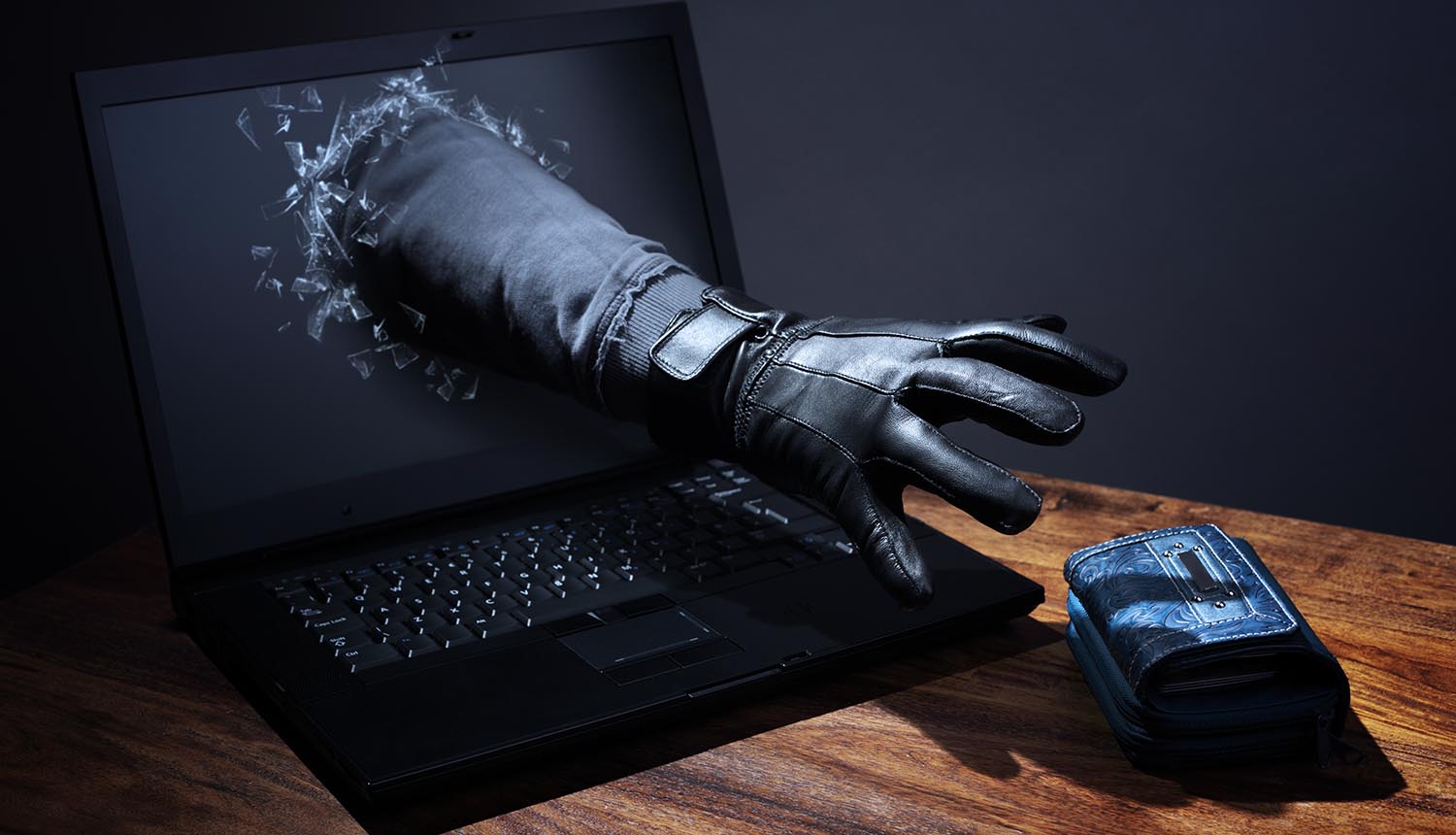
Small businesses remain a prime target for cybercriminals, with 43% of all cyberattacks focused on them. As ransomware attacks alone have surged by 62% since 2022, the risks have grown exponentially. With such stark numbers, businesses—especially smaller ones—cannot afford to overlook cybersecurity. Failing to address these threats can result in financial ruin and long-lasting reputational damage.
This guide provides an in-depth look into safeguarding your business by managing risks, leveraging advanced technologies, and fostering a culture of security. The statistics speak for themselves: 60% of small businesses close their doors within six months of a cyberattack. Investing in a comprehensive security strategy is no longer optional; it is essential for survival.
Understanding the Current Cyber Threat Environment
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly shifting, presenting new and more complex challenges for businesses. Below are key areas of concern:
1. Ransomware Attacks
- Prevalence: Reports show that 37% of organizations experienced ransomware attacks in the last year alone.
- Double-Extortion Tactics: Modern ransomware encrypts your data and simultaneously steals it, threatening to expose sensitive information unless a ransom is paid.
2. Phishing Attacks
- Cause of Breaches: Around 90% of data breaches stem from phishing, where attackers trick employees into revealing confidential data.
- Solution: Training employees to recognize phishing attempts and implementing email filtering tools can drastically reduce these incidents.
3. Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
- Increased Risks: 62% of businesses report heightened supply chain vulnerabilities in the last two years.
- Key Challenge: Third-party vendors often lack robust security measures, becoming weak links in your business’s security.
4. Zero-Day Exploits
- Delayed Patching: Half of all organizations struggle to patch vulnerabilities within 30 days of discovery, leaving systems exposed.
- Impact: Quick updates could prevent most exploitations, yet delays remain a common issue.
5. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
- State-Sponsored Attacks: 70% of APTs target critical infrastructure and are backed by governments.
- Emerging Concern: AI-driven attacks are making these intrusions harder to detect.
6. Fileless Malware
- Hard to Detect: 60% of businesses reported these stealthy attacks, which bypass traditional antivirus software.
- Need for EDR: Advanced endpoint detection systems are crucial for monitoring and mitigating such threats.
Why IT Security Is Critical for Businesses
Investing in IT security protects not just your data but also your reputation and customer trust. Consider the following key points:
The Financial Cost of Breaches
- The average cost of a data breach in the U.S. is $9.44 million, significantly higher than the global average.
- Small businesses often face closure due to financial strain following attacks.
Regulatory Compliance
- Laws like GDPR and HIPAA mandate stringent security practices, reducing risks of hefty fines.
Industry-Specific Risks
- Manufacturing, finance, and insurance industries are particularly vulnerable due to the sensitive data they handle.
| Metric | Impact |
|---|---|
| Average breach cost (US) | $9.44 million |
| Percentage of small businesses attacked | 43% |
| Compliance with GDPR/HIPAA | Reduces risk of legal and financial penalties |
Essential Cybersecurity Solutions
Implementing the right tools and technologies can significantly reduce risks. Below are some critical solutions:
| Cybersecurity Solution | What it Does | Advantages |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Adds extra layers of verification | Prevents 99.9% of unauthorized access |
| Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) | Uses AI to detect zero-day threats | Provides superior threat detection |
| Data Encryption | Secures data in transit and at rest | Prevents 80% of data exposure |
| Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) | Monitors device behavior | Reduces threat detection time by 50% |
| Email Gateway Security | Filters spam and harmful emails | Blocks 99% of malicious emails |
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA ensures that users must pass multiple verification steps, making it nearly impossible for attackers to gain access with just stolen credentials.
Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs)
These firewalls incorporate machine learning to detect advanced threats, such as zero-day vulnerabilities that traditional firewalls miss.
Data Encryption
Encrypting sensitive data ensures that even if it is intercepted, it cannot be read without the proper decryption key.
Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR)
By analyzing endpoint behavior, EDR can identify unusual activities and mitigate threats in real time.
Email Gateway Security
This tool filters out malicious emails, preventing phishing attempts and malware delivery at the inbox level.
Best Practices for Business Security
Adopting proactive measures can significantly enhance your cybersecurity posture. Here are some key practices:
Regular Software Updates
- Benefit: Updates fix known vulnerabilities, addressing 60% of security issues.
- Tip: Enable automatic updates to ensure timely patching.
Password Management
- Risk: Weak passwords are a common entry point for attackers.
- Solution: Implement strict policies and use password managers to generate strong credentials.
Comprehensive Data Backup
- The 3-2-1 Rule: Maintain 3 copies of your data on 2 different media types, with 1 stored off-site.
- Result: Protects against ransomware and hardware failures.
Employee Training
- Impact: 90% of breaches are due to human error.
- Approach: Conduct regular training sessions on recognizing phishing and adhering to security protocols.
Incident Response Plan
- Current Gap: Only 35% of businesses have formal response plans.
- Benefit: Such plans enable swift action during a breach, minimizing damage.
Building a Security-Focused Workplace
Employee Training
- Regular training reduces risks caused by employee mistakes.
- Example: Teach staff how to identify phishing emails and handle suspicious attachments.
Open Communication Channels
- Encourage employees to report security concerns without fear of reprisal.
Leadership Commitment
- Management’s active involvement in security initiatives fosters a culture of accountability.
| Statistic | Implication |
| 82% of breaches are human-related | Highlights importance of training |
| 36% of employees admit security mistakes | Ongoing education is critical |
| 21% do not report errors | Emphasizes need for better communication |
Importance of Regular Security Audits
Key Benefits
- Identify and address vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
- Improve compliance with standards like ISO 27001.
Types of Audits
| Type | Advantages |
| Internal Audits | Regular checks; identifies immediate issues |
| External Audits | More objective; uncovers additional weaknesses |
Impact of Audits
- Reduces breach risk by 30%.
- Lowers downtime by 25%, ensuring smoother operations.
Physical Security Measures
Key Strategies
- Access Control: Restrict sensitive areas to authorized personnel.
- Surveillance Systems: Use CCTV and motion detectors for continuous monitoring.
- Security Guards: Reduce incidents by 30%.
| Measure | Impact |
| Biometric Systems | Enhances accuracy by 70% |
| CCTV Surveillance | Deters crime by over 50% |
| Alarm Systems | Reduces theft response time by 40% |
Risk Management Strategies
Proactive Approaches
| Strategy | Description | Benefits |
| Risk Avoidance | Avoid high-risk activities | Lowers exposure to vulnerabilities |
| Risk Mitigation | Reduce the impact of risks | Minimizes damages during incidents |
| Risk Acceptance | Manage unavoidable risks | Balances flexibility with preparedness |
| Risk Transference | Use insurance to cover major risks | Reduces financial strain after events |
Summary
Cybersecurity in 2025 is about being proactive and prepared. By understanding the current threat landscape, implementing advanced tools, and fostering a culture of security awareness, businesses can protect their assets and reputation. Regular audits, employee training, and risk management are vital components of a robust cybersecurity plan. Taking these steps ensures resilience against evolving threats, safeguarding both digital and physical operations.
Data analytics expert. As an analyst and project manager, I have proven to be a strong leader and team player in maintaining a suitable workspace for workers and industries in the oil and gas sector.
By taking into account various factors, with the assistance of state of the art technologies and the utilization of Big Data Analytics.
This includes considering various aspects like volume, velocity, variety, veracity, value together with complexity.
With the recent advent of data recording sensors in exploration, drilling, and production operations, oil and gas industry has become a massive data intensive industry.